| |
How Internet Services security works
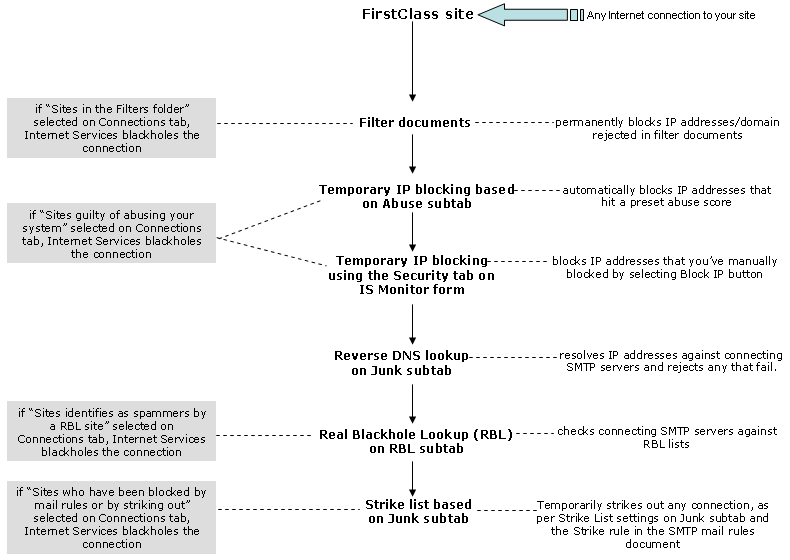
Internet Services security features are layered and execute in this order:
1 SMTP AUTH, which verifies credentials for POP3 and IMAP4 clients to relay off your FirstClass site.
2 Filter documents, which accept or reject mail based on the sender's IP address or domain name that appears in your filter documents.
3 IP automatic block, which automatically blocks IP addresses (temporarily) that reach a preset score based on the Abuse subtab settings on the UCESpam tab on the Basic Internet Services form. You can also set the duration you want to block the IP address on the Abuse subtab.
4 IP temporary block, which manually flags suspicious IP addresses, which you can view on the Security tab on the
Internet Services Monitor form. You can manually block the offending IP addresses once you've identified them.
5 Reverse DNS Lookup, which queries the DNS name against an incoming IP address for validity, if you have it this option enabled on your system (Junk subtab on the UCE/Spam tab on the Basic Internet Setup form).
6 RBL (Realtime Blocklists) lookup and SURBL (Spam URI Blocklists), which queries the RBL services of your choice (RBL subtab on the UCE/Spam tab on the Basic Internet Setup form).
7 SMTP rules, which scans and inserts a message header, message body, and spam score (assigns a number) to incoming email based on its content.
8 User-created rules (Setting up automatic mail handling), which handle incoming mail based on a user's personal mail rules (see Client help).
For more information
| ||